Lets get less criticable
and start getting to the point...
It has been seen that SNA SNB and other classical cephalometries elements do not correspond to a physiological "reality". Let's see how to better define some normal anatomical relationships.
Delaire's base of the skull
It also has been seen that S is instable in time, beside being a soft tissue point used to represents bones.
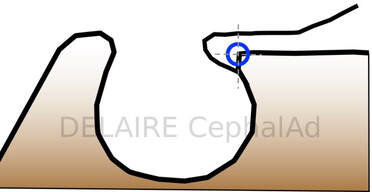
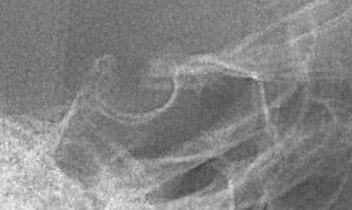
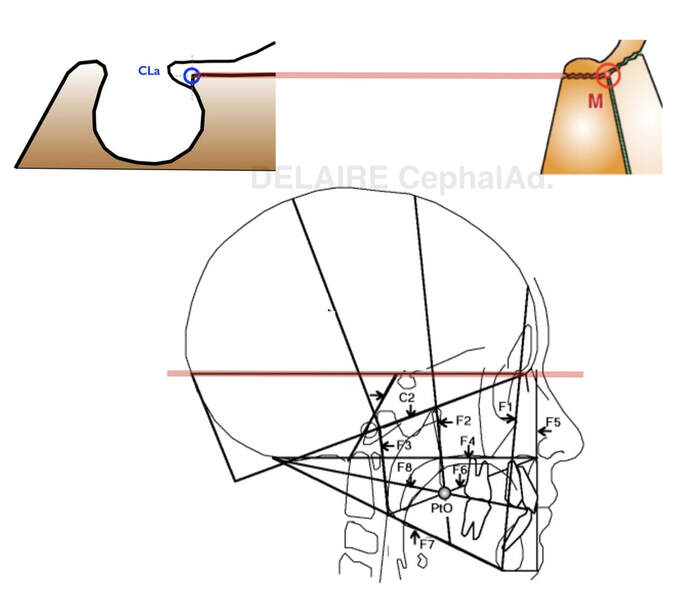
Anterior clinoid point Cla (posterior landmark of Delaire's base of the skull)
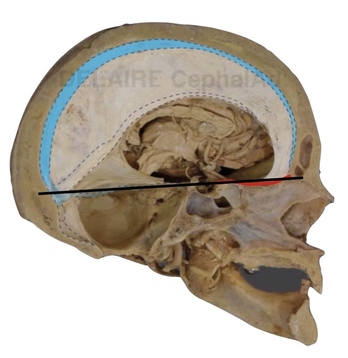
It is better to use Delaire's Cla point, at the base of the anterior clinoid process opposite to the most anterior concave portion of the sella. This corresponds to the point facing the superior aspect of the image of the optic canal, and, most anterior concave margin of the sella (click above).
The intersection of the lower part of the anterior clinoid process and the anterior margin of the sella is said the most fixed part of the sella by A. BJÔRK & B. MELSEN.
Delaire's base of the skull
It also has been seen that S is instable in time, beside being a soft tissue point used to represents bones.
Anterior clinoid point Cla (posterior landmark of Delaire's base of the skull)
It is better to use Delaire's Cla point, at the base of the anterior clinoid process opposite to the most anterior concave portion of the sella. This corresponds to the point facing the superior aspect of the image of the optic canal, and, most anterior concave margin of the sella (click above).
The intersection of the lower part of the anterior clinoid process and the anterior margin of the sella is said the most fixed part of the sella by A. BJÔRK & B. MELSEN.
|
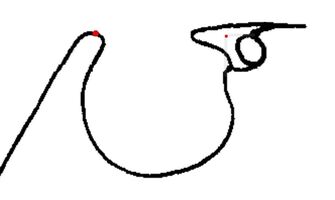
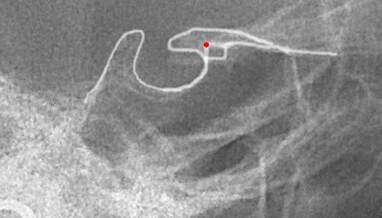
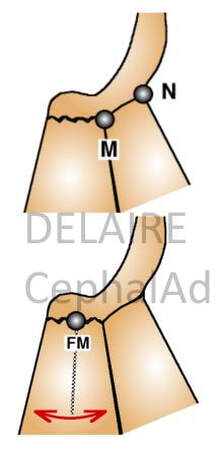
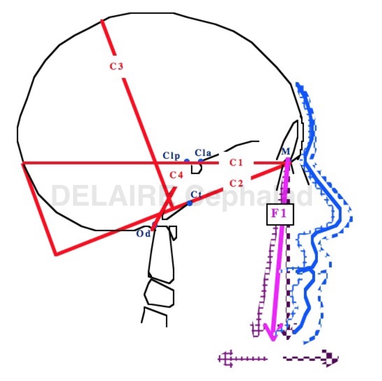
M point ( anterior limit of Delaire's base of the skull)
Displacements of N (fronto-nasal point) have no value with regard to the sagittal maxillary development. It is better to use the M Point (metanasion), located at the junction of the fronto-nasal, maxillo-nasal and fronto-maxillary sutures, and which represents the true anterior limits of the base of the skull. To objectify the maxillary rotations, the best recording point is FM, located in the middle of the Fronto-Maxillary Suture /articulation. Once again, N cannot be used to represent the base of the skull. It's physiologicla relevance only applies to vertical facial developments (in which the Fronto-nasal Suture actively participates). The N point should therefore be retained, exclusively, for measurements concerning the vertical dimensions of the facial skeleton. From here Delaire's base of the skull (C1 : first cranial line) can be drawn from Cla to M. This line overlaps a very stable structure as precised by de Coster. |
|
|
Instead of using SNA & SNB which have nothing to do with the maxilla & mandible to evaluate their positions and inter relationships, let's see this from a Delaire's point of view.
How to define/ modelize the maxilla and the mandible ?
How to define/ modelize the maxilla and the mandible ?
|
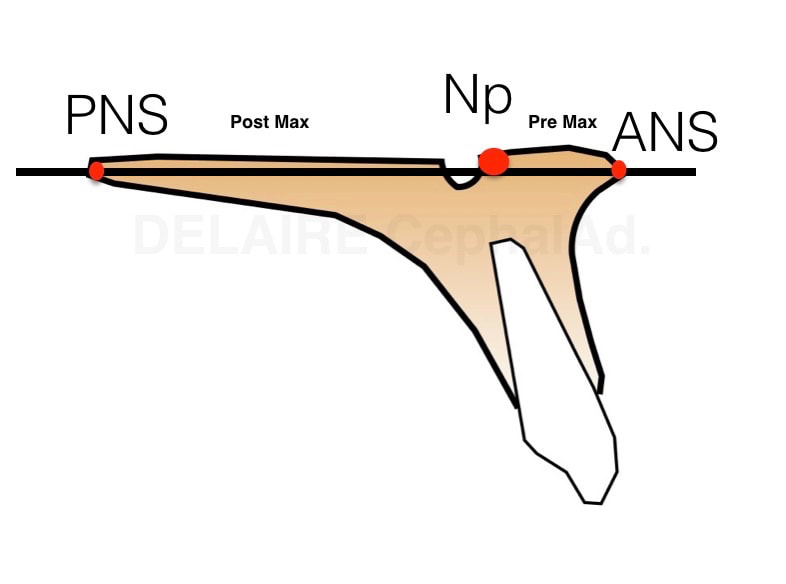
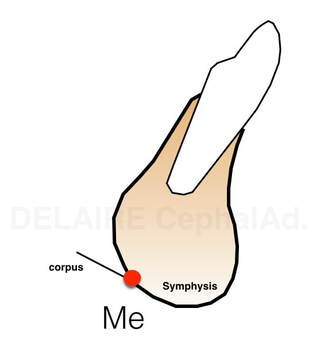
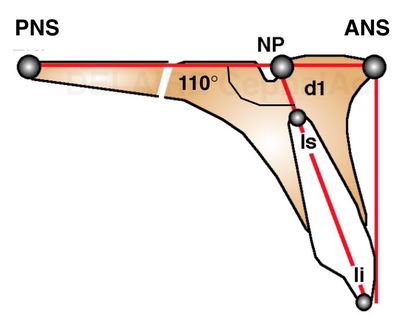
The maxilla can/must be defined by the posterior nasal spine (PNS) and the anterior nasale spine (ANS). This line modelizing the bas of the maxilla passes thru the anterior aspet of the naso palatine canal. It allows to define a pre and post maxilla, normally aligned. The mandible can simply be defined by Delaires's Menton point (Me). It isn't the lowest point of the symphysis. It is the intersection of the image of the lower border of the symphysis, and the image of the lower border of the ramus. |
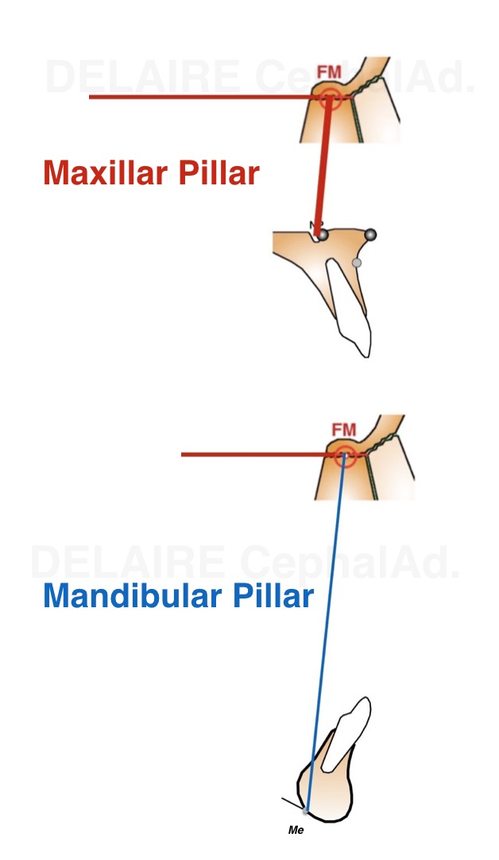
Defining the base of the skull, the maxilla and the mandible, allows to precise their reciprocal relationships. Delaire uses a maxillar pillar and a mandibular pillar, which of course, normally shoul overlap.
.
Maxillar pillar.
It is a line modelinzes the path of the occlusal forces which diffuse in the bone. It is drawn from FM, middle of the maxillo frontal suture to NP, anterior aspect of the naso palatine canal (ie the limit between the two maxillas).
Mandibular pillar.
Again, It is a line modelizing the path of the occlusal forces which diffuse in the bones and through the teeth. It goes from FM to Me.
Maxillar pillar.
It is a line modelinzes the path of the occlusal forces which diffuse in the bone. It is drawn from FM, middle of the maxillo frontal suture to NP, anterior aspect of the naso palatine canal (ie the limit between the two maxillas).
Mandibular pillar.
Again, It is a line modelizing the path of the occlusal forces which diffuse in the bones and through the teeth. It goes from FM to Me.
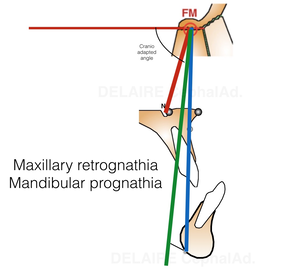
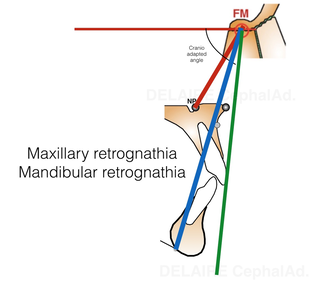
The maxilla and the mandible can be correctly aligned :
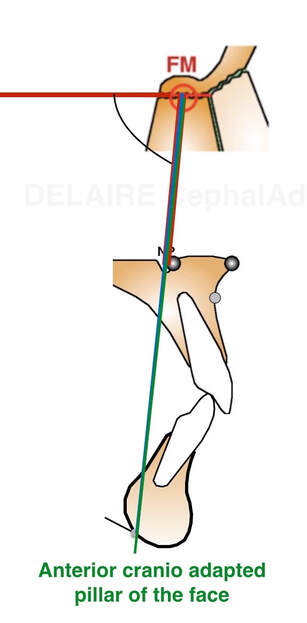
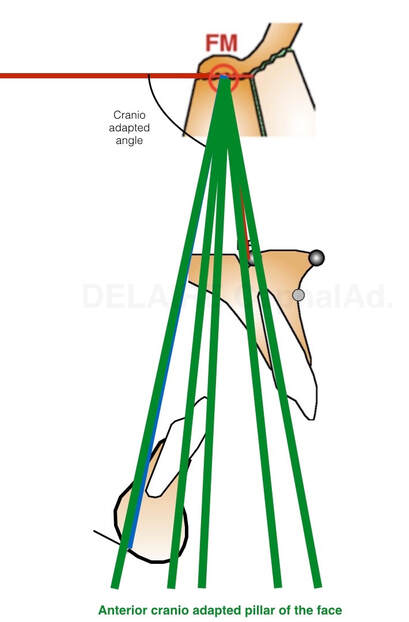
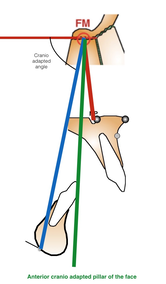
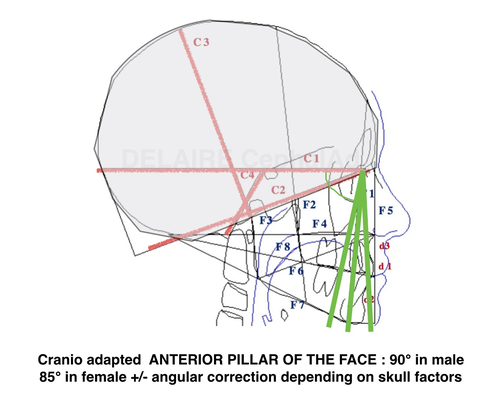
Anterior cranio adapted pillar of the face
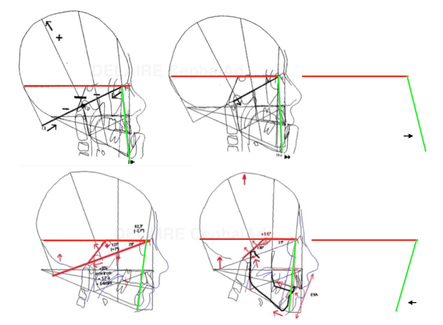
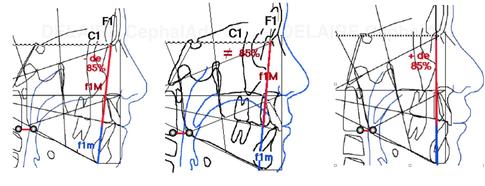
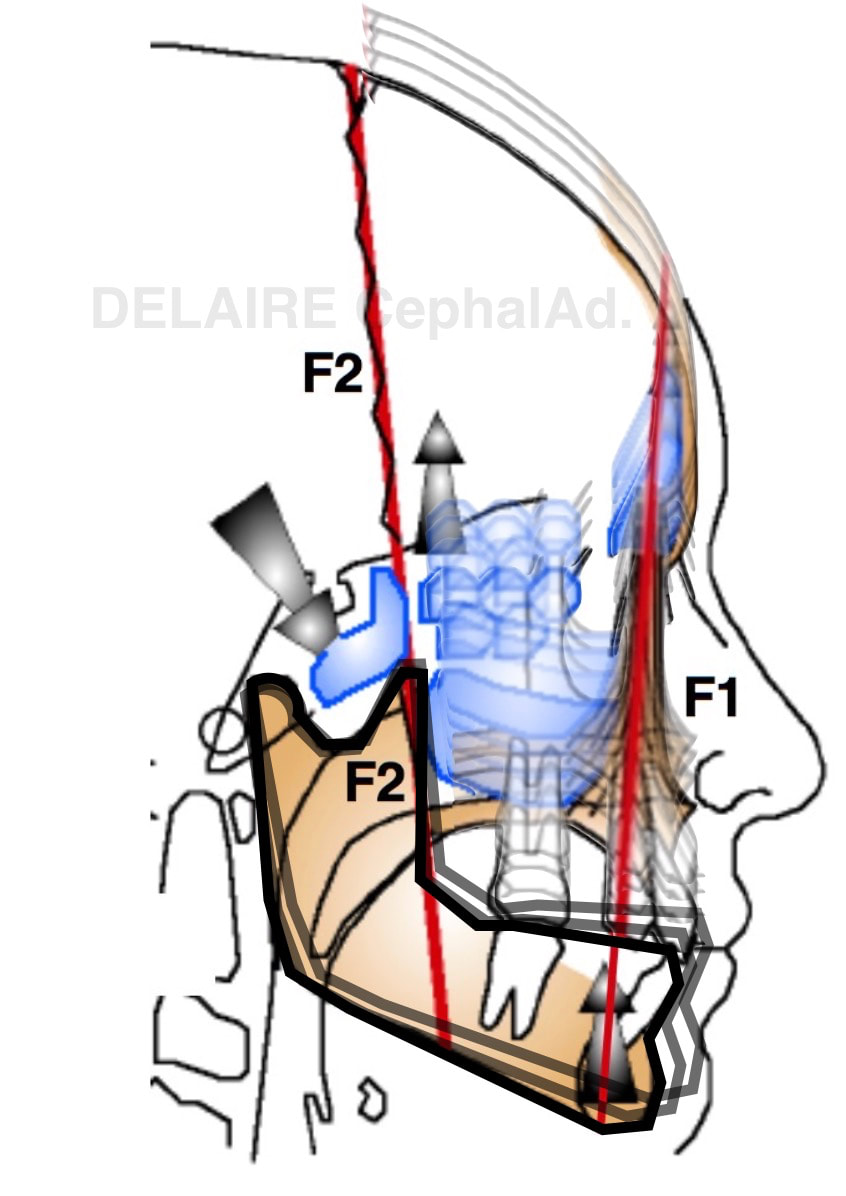
The angulation between F1 anterio pillar of the face, and Delaire's base of the skull C1 is normally : 90° in male, 85 in female and kids, reflecting the mote projected (transfrontal) profiles upon sex and age. The delaire approach individualizes the plot by adding or subtracting a correction factor to this normal angle. This corrective factor is calculated according to different values measured on the skull and describing its overall shape. Indeed, the skull can have a shorter base, and be globally higher, predisposing to a class 3, or inversely, be longer but less high and predisposing to a class 2, this being partly related to the position of the TMJ induced by these cranial conformations.
This pillar will determinate and personalize all the Delaire's cephalometric analysis making it a personnalized tool which will adapt itself to respect the particularities of the growth of the subjects according to the sex.
The angulation between F1 anterio pillar of the face, and Delaire's base of the skull C1 is normally : 90° in male, 85 in female and kids, reflecting the mote projected (transfrontal) profiles upon sex and age. The delaire approach individualizes the plot by adding or subtracting a correction factor to this normal angle. This corrective factor is calculated according to different values measured on the skull and describing its overall shape. Indeed, the skull can have a shorter base, and be globally higher, predisposing to a class 3, or inversely, be longer but less high and predisposing to a class 2, this being partly related to the position of the TMJ induced by these cranial conformations.
This pillar will determinate and personalize all the Delaire's cephalometric analysis making it a personnalized tool which will adapt itself to respect the particularities of the growth of the subjects according to the sex.
|
F2.
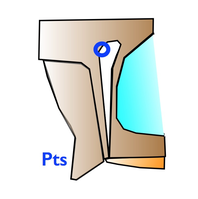
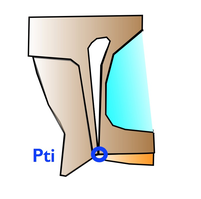
F2 represents the dissipation line of the occlusal forces. When the mandible hits the maxilla, the resulting forces a dissipated along the F1 line anteriorly, and F2 posteriorly. This explains the persistance of the coronal suture until late in life. F2 is of tremendous importance in determining the ideal theorical occlusal plane of the patient. F2 is drawn with 2 points : the inferior pterygoid point Pti, and the superior pterigoid point Pts. If Pts is difficult to mark, the image of the bregma can be used. This line particularly represents the physio-mechanical principles of Delaire |
|
Dental lines and Pogonion
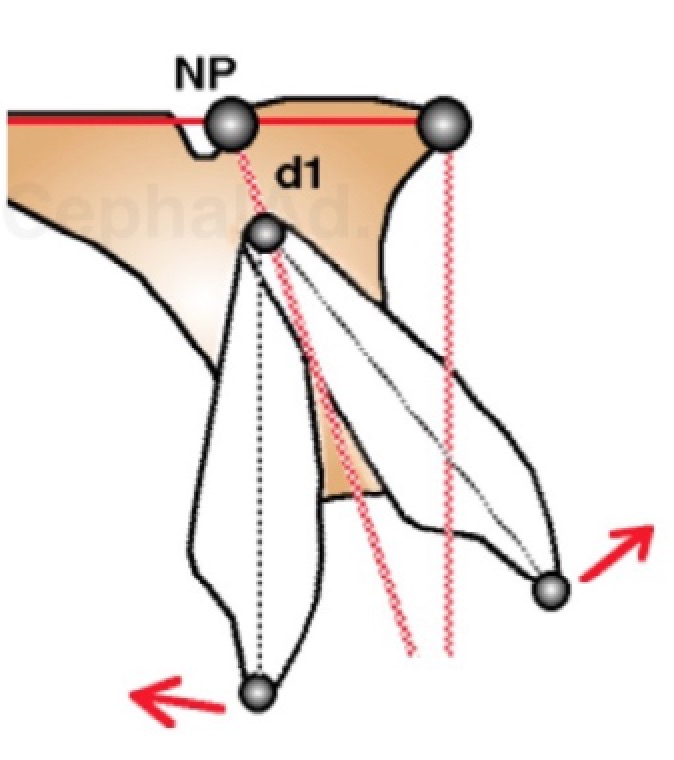
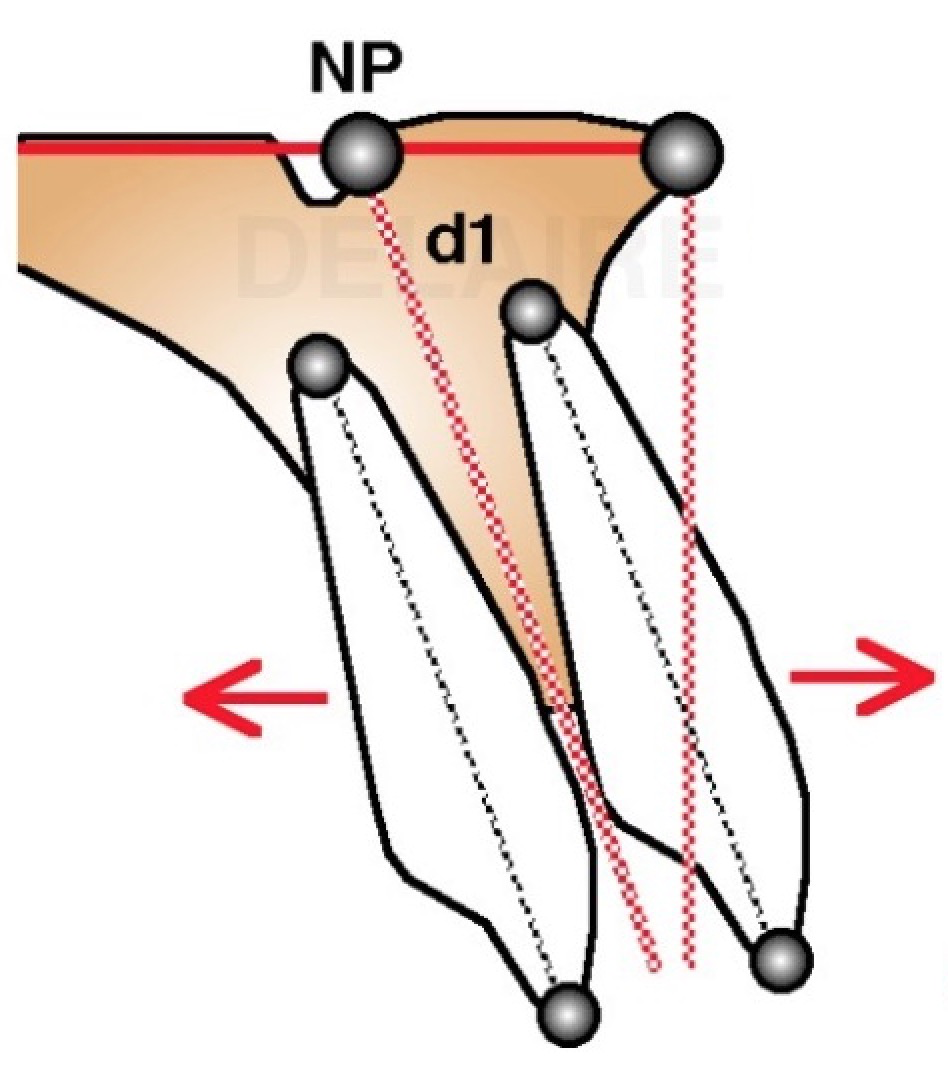
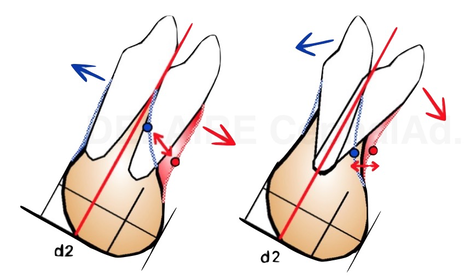
Maxillar dental line Dental axes are easy to trace. Teeth do have a ideal normal location on their osseous base. In this approach, the axe of the upper central incisor d1 passes by Np. making a 110 degree angle with the palatine base (PNS-ANS). Ideally, the vertical line drawn perpendicular to PNS-ANS is tangent to the free border of the upper central incisor crown. (1m) The upper central incisor can be rotated compared to its ideal axe (2m). We will speak about incisor Version ( aka : labio or palatal version). It can be globally translated compared to its ideal axe (3m). We will speak about Position (aka labio or palatal position, aka2 pro or retro alveolia). Or it can present a combinaison of this 2 movements. We are speaking about abnormalities compared to an ideal state. |
|
REMARQUE:
Checking internet, we can state how imprecise the notions and concepts we are dealing with on an every day basis are. Here the french word "proalvéolie" (i.e. pro alveolia) is translated as "labio-version" OR "open bite", both having nothing to do with a pro alveolia as logically defined by Delaire. |
|
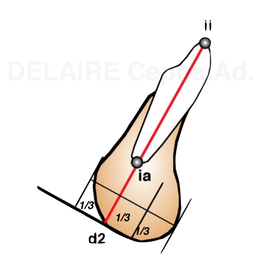
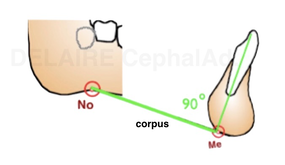
Mandibular dental line The same way we can define the axe d2 of the lower central incisor. We can define the base of the corpus, defined by the line linking No, notch and Me. The lowest point of the ramus depending on functionnal factors, we should avoid its use. Ideally, the axe of the incisor should be in the middle of the posterior two third of the symphysis , should pass by Me and make an 90° angle with No-Me. The posterior two thirds represent the real base of the symphysis. The anterior one third is : functionnal and appositionnal. Compared to this ideal position, the same abnormalities can be described, and quantified. |
|
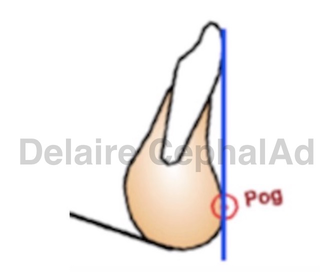
Pogonion.
Pog has nothing to do with S... nothing. They"ve never been introduced. Pog represents inderectly the constitutional amount of mandible bone derived from the first arch, and the functionnal response of this bone to local muscle activity. The lower incisor being correctly placed on the symphysis, the perpendicular line to C1 passing by the free border of the incisor shoud be tangent to the symphysis in Pog. |
All these elements comparing the actual anatomy of the patient to an ideal state/ architecture
allow to go further in our process....
allow to go further in our process....
end of section