Relevant elements in sagittal radiological face evaluation
|
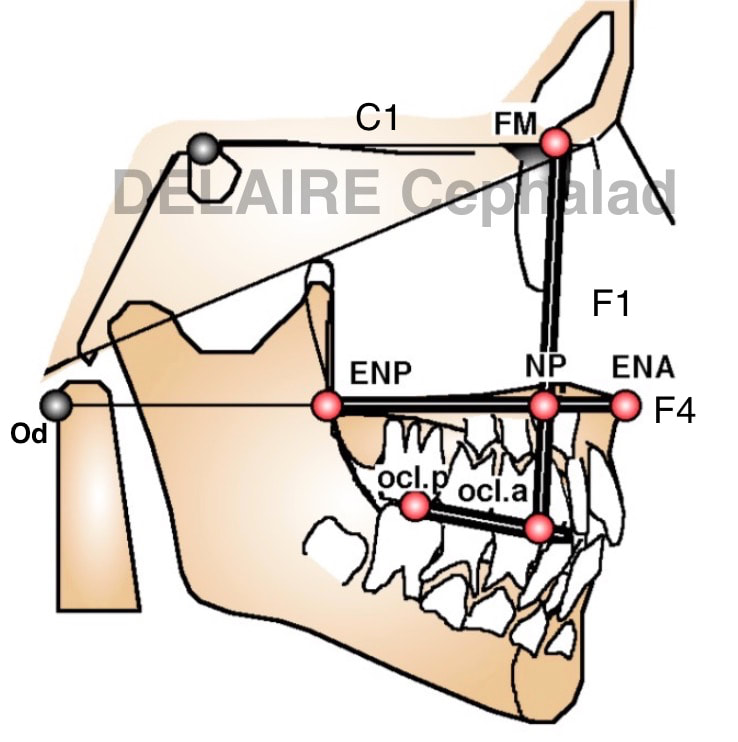
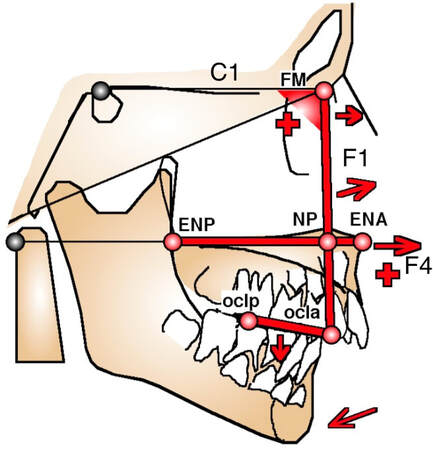
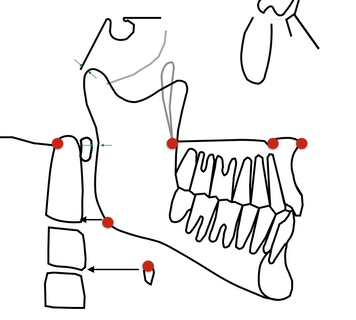
Segments allowing to evaluate the maxilla. 3 segment allow to evaluate the state of maxilla in the cranio facial ensemble : - FM-Np ( F1) and its angulation with C1 for the sagittal position - ENP (PNS) ENA (ANS) F4 in relationship to Od. ENP ENA and Od should normally be aligned, giving the normal vertical level of the palate. - Oclp-Ocla (posterior occlusal point on the first superior molar & anterior occlusal point between the 1st & 2nd premolar) giving the position and inclinaison compared to the maxillar base of the maxillar occlusal plane . Example. |
|
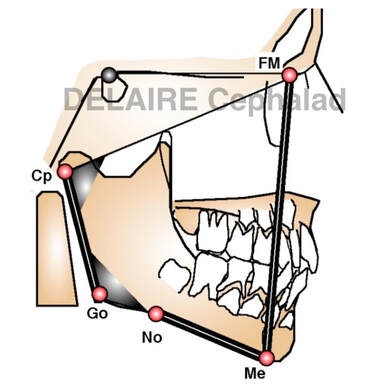
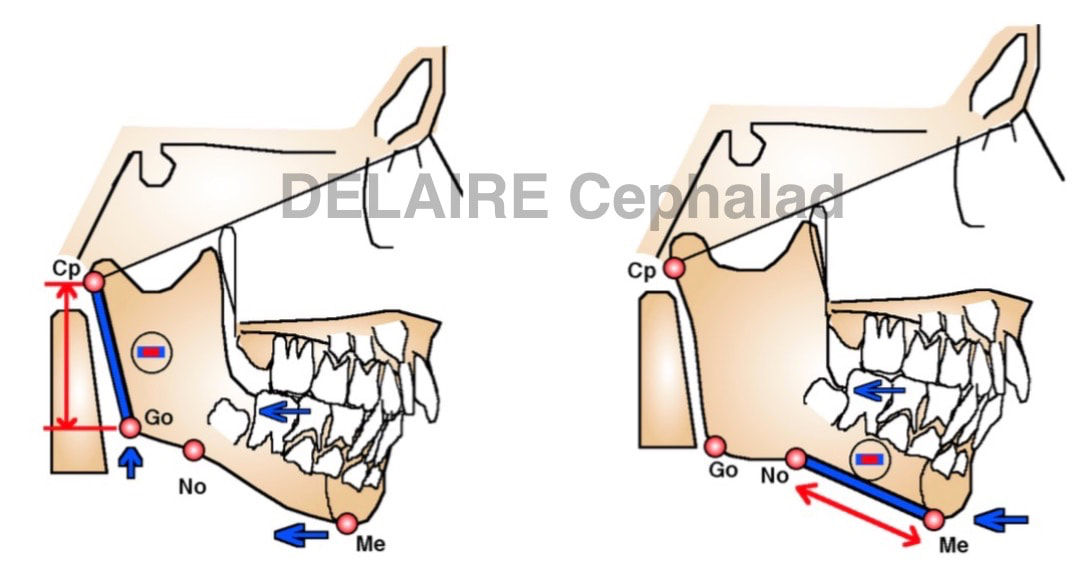
Segments allowing to evaluate the mandible. 3 segments allow to evaluate the mandible : - FM-Me giving the sagittal position compared to the base of the skull - Me-No ( notch) representing the base of the corpus - Go (gonion)- Cp (condylar point) representing the base of the ramus, which length and orientation define de ramus One extra relevant information : - the angle Cp-Go / No-Me Example. |
|
Normal vertical levels.
Normally : - the angle of the mandible is on the vertical level of the antero inferior angle of the 2nd cervical vertebra. - the body of hyoid bone is on the same level than the antero inferior angle of the 3nd cervical vertebra ( otherwise we are in presence of a mouth breathing and/or myopathic patient) - the palate should be on the level of the Od point already seen. Od, PNS, ANS, Np should normally be aligned. Bonus information : - the ramus should never overlap the anterior arc of C1 (meaning compromised airways) - the head of the condyle should never cross the image of occiput (meaning a wrong position of the temporal glenoid fossa in the facial architecture). |
|
Dental relevant elements
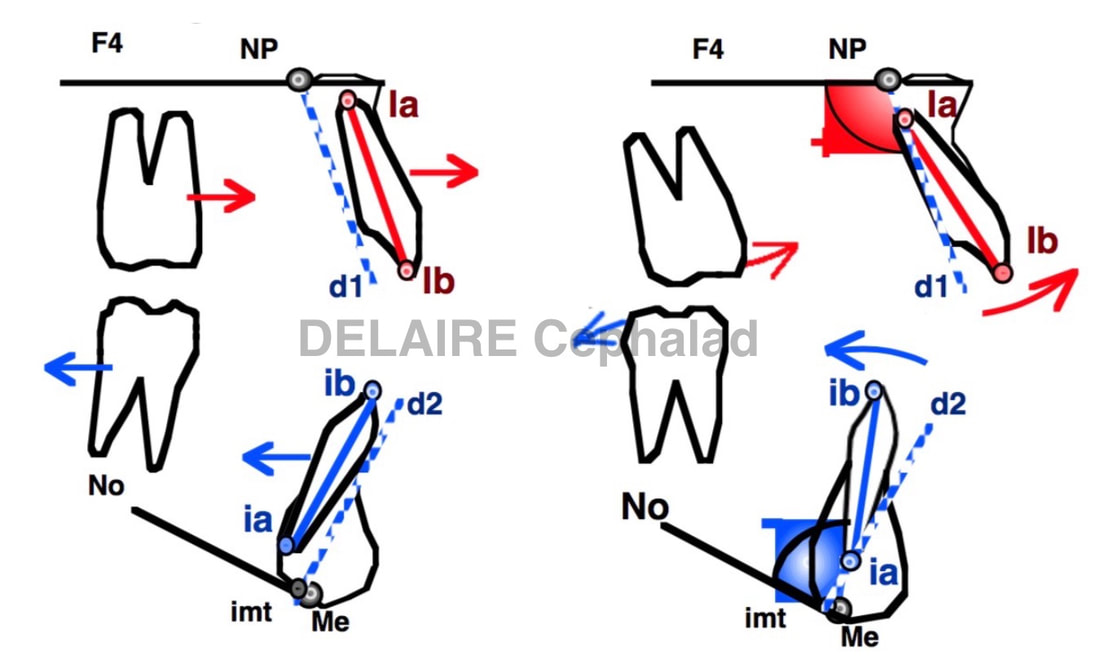
It has already been seen how to evaluate the position and versions of the incisors : see right for an illustration |
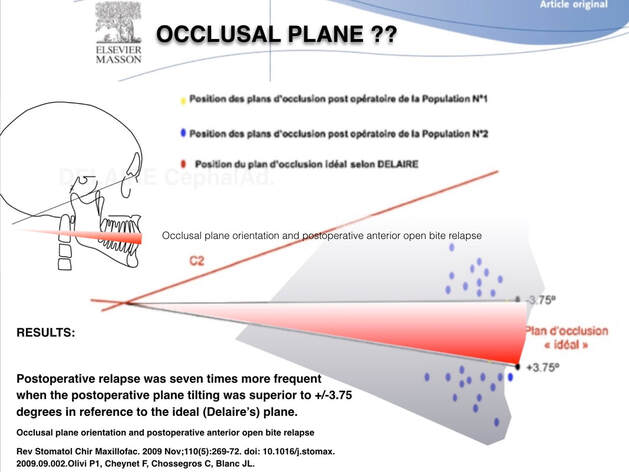
Occlusal plane
It has been shown that, in case of open bite, but further works should be done on that subject, if you surgically put the occlusal plane of the patient too far away from the theorical ideal one, relapse occurs.
see litt.
It has been shown that, in case of open bite, but further works should be done on that subject, if you surgically put the occlusal plane of the patient too far away from the theorical ideal one, relapse occurs.
see litt.
Cranial relevant informations
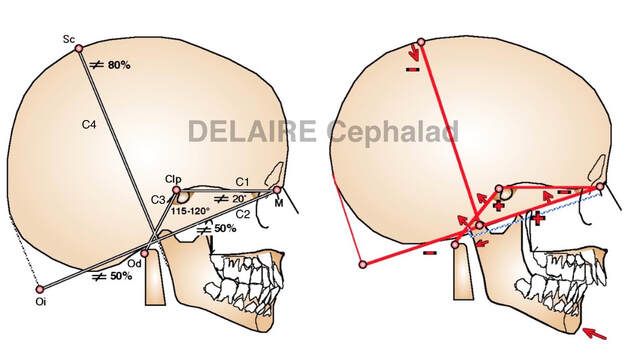
4 lines allow to evaluate the skull
C1
C2
C3
C4
- C1C2 determines the anterior angle of the base of the skull
- C1C3 determines the posterior angle of the base of the skull
- C4 is drawn form the middle of C2. It is the height of the skull expressed as a ratio from the lenght of C2. This ratio expresses the global shape of the skull (more round or more elongated)
- The distance between M and the intersection of C2 and the image of the posterior aspect of the condyle (Cp) defines two segments on C2. M-Cp and CP-Oi. M-Cp is the cranio facial segment. Cp-Oi is the cranio spinal segment. These 2 segments are normally equal. If for example M-CP > 50% of C2, the tmj will tend to be positioned further back in the ensemble leading to a class II. We are speaking in this case from cranial predisposition to a classe II. The same goes for a closure of the anterior angle of the base of the skull and/or an opening of the posterior one.
All this indirectly represents the effets of the aponeurotis tension system
The Open Dentistry Journal, 2009, 3, 100-113 The Aponeurotic Tension Model of Craniofacial Growth in Man Richard G. Standerwick1,* and W. Eugene Roberts2
4 lines allow to evaluate the skull
C1
C2
C3
C4
- C1C2 determines the anterior angle of the base of the skull
- C1C3 determines the posterior angle of the base of the skull
- C4 is drawn form the middle of C2. It is the height of the skull expressed as a ratio from the lenght of C2. This ratio expresses the global shape of the skull (more round or more elongated)
- The distance between M and the intersection of C2 and the image of the posterior aspect of the condyle (Cp) defines two segments on C2. M-Cp and CP-Oi. M-Cp is the cranio facial segment. Cp-Oi is the cranio spinal segment. These 2 segments are normally equal. If for example M-CP > 50% of C2, the tmj will tend to be positioned further back in the ensemble leading to a class II. We are speaking in this case from cranial predisposition to a classe II. The same goes for a closure of the anterior angle of the base of the skull and/or an opening of the posterior one.
All this indirectly represents the effets of the aponeurotis tension system
The Open Dentistry Journal, 2009, 3, 100-113 The Aponeurotic Tension Model of Craniofacial Growth in Man Richard G. Standerwick1,* and W. Eugene Roberts2
end of section